Remote Work Glossary
- Results for "undefined"
Table of Contents
What is a global HRIS?
Who uses an HRIS?
How does an HRIS help an organization?
What are the benefits of HRIS?
What are the types of HRIS systems?
What are the key features of an HRIS?
What does it mean when an HRIS integrates with existing tools?
How does an HRIS work?
What are examples of HRIS systems?
When should an organization get an HRIS?
What is HRIS implementation?
What are the challenges of implementing an HRIS, and how can they be addressed?
How can HR managers measure the ROI of an HRIS implementation?
Manage your global workforce compliantly with Deel
What is an HRIS system?
An HRIS, which stands for Human Resource Information System, is a digital system or software solution that enables companies to store, organize, and manage all workers’ (employees, contractors, or freelancers) data through a centralized database. It consolidates all information together to streamline the key HR processes.
An HRIS streamlines HR processes, improves data accuracy, and helps organizations make informed decisions by providing key workforce insights.
What is a global HRIS?
A global HRIS is built to support HR operations across multiple countries, managing the complexity of cross-border employment.
Key traits of a global HRIS include:
- Handles multi-country compliance, contracts, tax, and benefits
- Supports multiple currencies, languages, and time zones
- Centralizes data from globally distributed teams
- Integrates with global payroll, immigration, and EOR providers
- Enables standardized processes across regions, while allowing for local flexibility

Example use case: A company with employees in 15 countries uses a global HRIS to unify document management, time off management, eporting, and onboarding, while respecting each country’s local laws and practices.

Case Study
We couldn't find a global HRIS. So we built our own.
What is a local HRIS?
A local HRIS is designed to manage HR operations within a single country or region. It is optimized for local compliance, language, currencies, and labor laws.
Some of the key traits of a local HRIS are:
- Supports only local employment laws and tax rules
- Often designed around one language and currency
- Integrates with domestic payroll and benefits providers
- Works well for companies that operate in just one country
Example use case: A U.S.-based company with all employees in the U.S. might use a local HRIS that supports U.S. tax forms, health insurance integrations, and state-level labor laws.
Who uses an HRIS?
HR, managers, and workers use HRIS for day-to-day human resources functions. HR professionals use HRIS to automate processes like leave management, time-tracking, and HR reporting.
Managers access team members’ information during performance reviews and approve leave requests. Workers use the HRIS to apply for leave, check company policies, or download their documents.
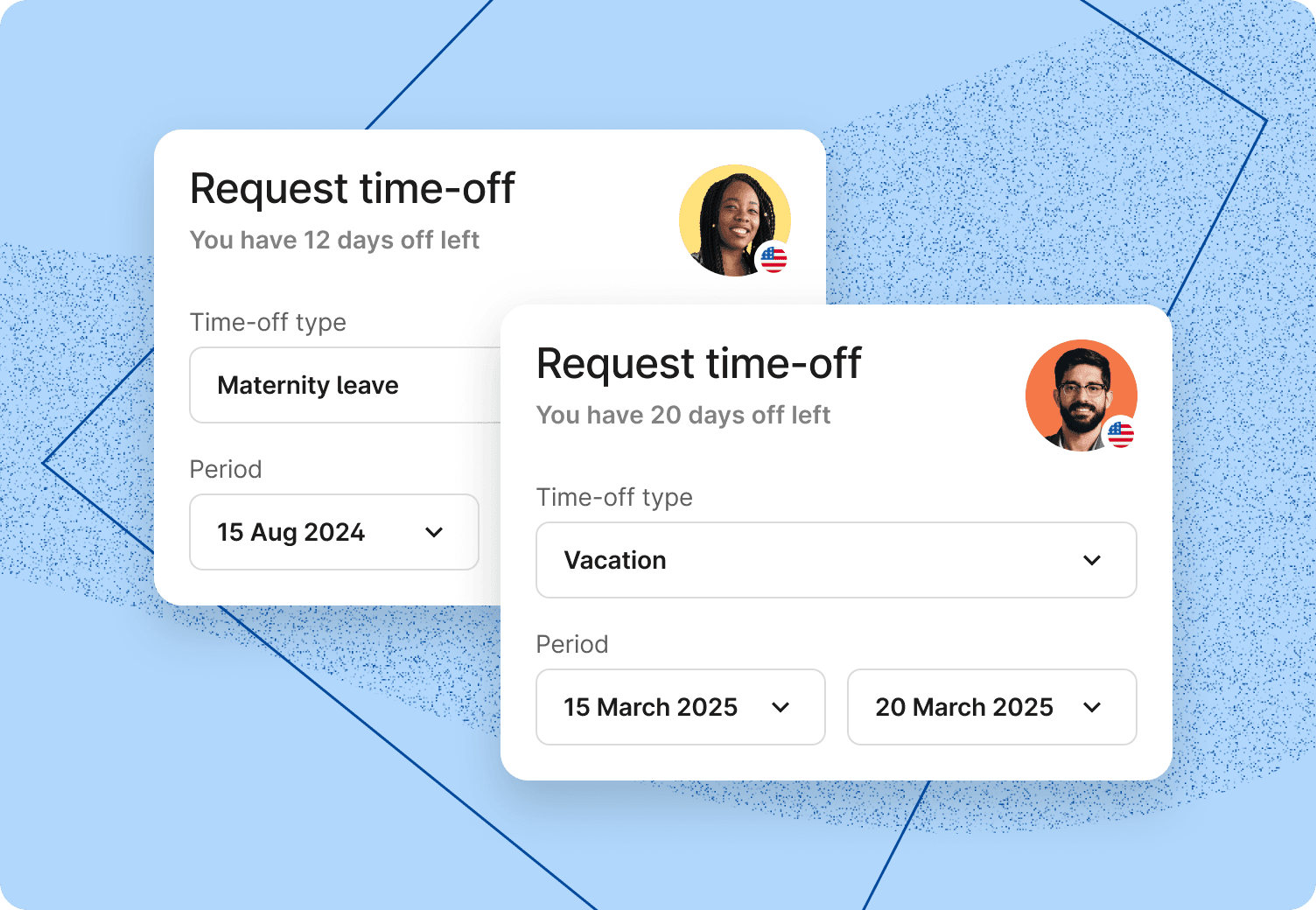
How does an HRIS help an organization?
An HRIS helps an organization by centralizing all workers’ data required to perform key HR functions. It reduces the manual work of HR and helps them focus more on strategic tasks. It also enhances the worker experience by providing them with self-service options. Workers can submit common requests, such as applying for leave and downloading documents, directly in the portal, eliminating the need to contact HR. HRIS saves time for both HR and workers by digitizing common tasks.
What are the benefits of HRIS?
An HRIS helps minimize common HR department challenges by automating tasks, strengthening compliance, and organizing HR data. Here’s a deeper look into the benefits of using an HRIS:
- More time for meaningful HR tasks: HR spends up to 57% of their time on administrative tasks, which could easily be automated. HRIS allows them to spend more time on strategic tasks.
- Better, data-driven decision making: Once you’ve migrated all of your data to an HRIS, you can start making data-informed decisions inspired by accurate information and real-time insights pulled from HR analytics.
- Reduced costs: Your HR team will see a reduction in costs due to shorter onboarding cycles, lower staff turnover, and higher worker productivity with automation. For example, HR software tools can reduce onboarding time by up to 80%.
- Enhanced data protection and compliance: Instead of spreading sensitive worker information across poorly-guarded spreadsheets, you can store all information securely on one HRIS. Most HRIS providers also regularly update to meet the latest cybersecurity requirements and data security standards.
- Improved worker experience: When you centralize and automate your HR processes in an HRIS, worker inquiries won’t get lost in the email inbox. Better handling of inquiries improves worker experience. HRIS also provides a self-serve option for easily raising any inquiries.
- Support for scaling businesses: Instead of separating workers’ information into multiple HR systems and spreadsheets, an HRIS centralizes it into one organized platform, accommodating an increasing amount of data and a growing number of workers.

How does an HRIS help with compliance management?
HRIS automates crucial compliance-related tasks, mainly:
- Accurate record-keeping: HRIS ensures that all employee information is up-to-date and centralized in one place, which is essential for audits.
- Supports local law adherence: HRIS automatically onboards and offboards workers in compliance with local laws. HRIS also tracks adherence to labor laws, including overtime regulations and leave requirements, thereby reducing the risk of violations.
- Improves data security: HRIS also securely stores data as per the data security standards and local laws.
- Automates compliance tracking and reporting: With an in-built HR analytics module, you can also generate compliance reports on the workers’ data.
What are the types of HRIS systems?
There are three main types of HR systems: Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS), Human Resources Management Systems (HRMS), and Human Capital Management (HCM). All three are closely linked but differ in functionality. Let’s see how:
- Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS): HRIS, as the name suggests, mainly focuses on bringing all the worker information into one platform. It does provide basic automation features like signing documents, time-tracking, leave management, and simple analytics. All advanced features, such as payroll management, benefits administration, and performance management, require add-ons or integrations.
- Human Resources Management Systems (HRMS): An HRMS includes the basic features of an HRIS and additional features for recruitment, benefits administration, payroll management, and more.
- Human Capital Management (HCM): HCM software is usually the most comprehensive option, building on the basic HRIS features with talent management tasks such as learning and development, performance management, succession planning, and more.
How is an HRIS different from an HCM or HRMS?
People often use the terms HRIS, HRMS, and HCM interchangeably due to their shared product features. These are all cloud-based HR software solutions that help HR departments manage their workforce, but offer different levels of service. HRIS focuses on record-keeping and managing simple HR processes. HRMS includes advanced features for benefits administration, payroll management, and more. HCM offers more strategic aspects for talent management by supporting learning, performance management, and succession planning.
Read more: HRIS vs. HRMS: Which Is the Right Fit for Your Organization?
What are the key features of an HRIS?
An HRIS typically includes the basic features for workers to get started in an organization, such as onboarding, policy management, HR document management, time-tracking, and more. Advanced features for talent acquisition, payroll processing, and learning management are available in HRMS or HCM as an add-on.
Key features available in HRIS solutions are:
- Employee data and document management: Companies get a centralized system for storing all worker records and documents (contracts, personal records, etc).
- Policy management: In addition to centralized worker data, people teams can also establish a single repository for company policies and handbooks.
- Employee self-service portal: Workers can easily access a self-service portal to submit simple requests, such as leaves, or download any necessary documents.
- HR process automation: People teams can automate HR tasks for handling onboarding, device provisioning, offboarding, or changing department/role of employees.
- People analytics: People teams and executives can easily pull out insights like headcount, salary/costs, or diversity metrics from your worker data.
- Time-off & absence management: People teams can define leave policies (according to local labor laws), approval workflows, and accruals rules. Managers and workers can check PTO balances and daily/weekly/monthly team availability.
- Org chart and hierarchy mapping: Everyone in the company can visualize roles, reporting lines, or team structures.
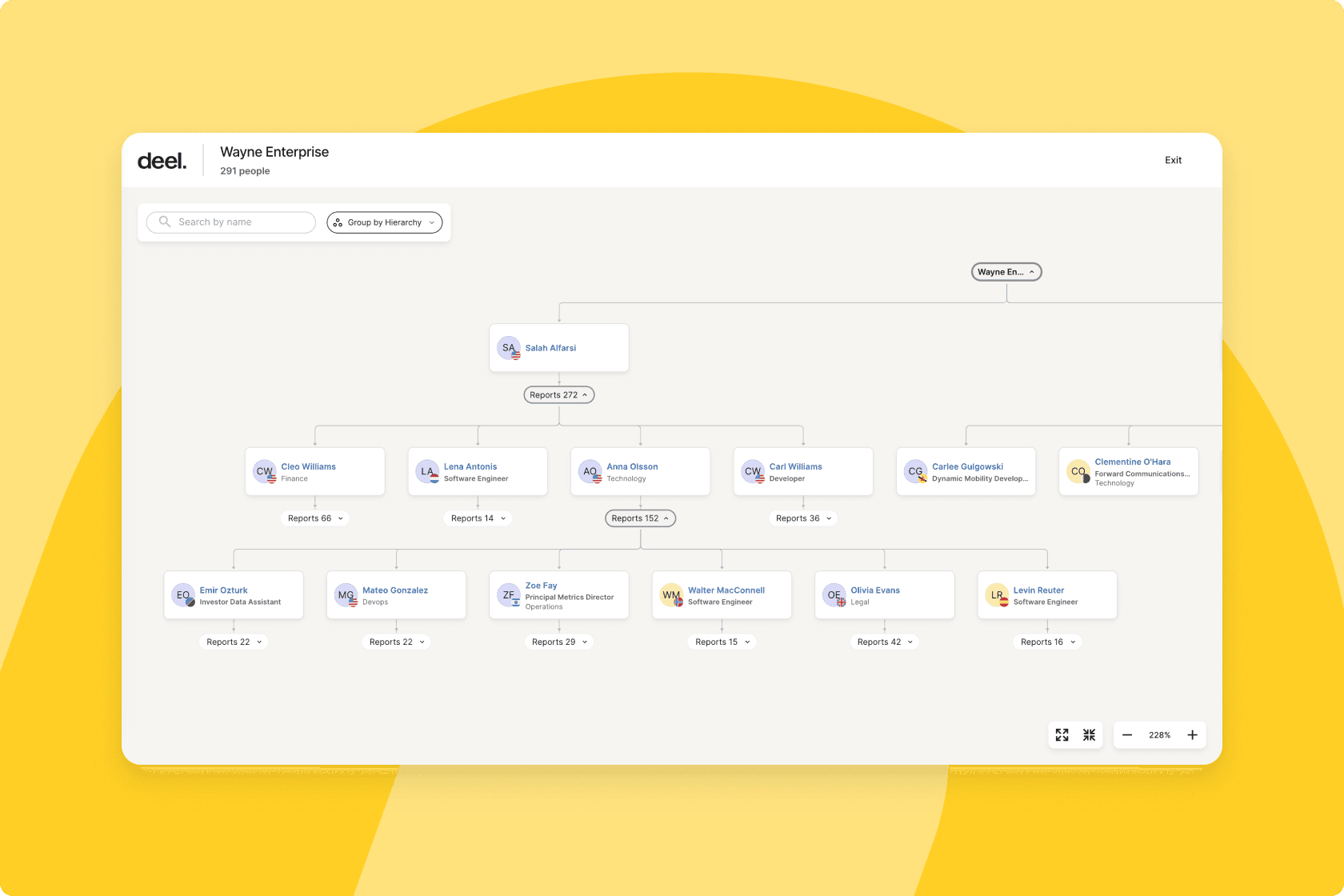
Common add-ons available in HRMS are:
- Payroll processing: Payroll is not available by default in HRIS. By bringing a payroll add-on, you can automate salary calculations, tax deductions, and direct deposits to global workers in compliance with local laws.
- Benefits administration: With the benefits module, you get an advanced tool that helps you connect with all benefits providers and design a benefits plan compliant with local laws.
- Recruitment management: Handling recruitment is another feature in HRMS with support for posting jobs, tracking applicants, conducting interviews, and managing candidate communication.
Common add-ons available in HCM are:
- Learning and development: HCM provides more advanced modules for talent management with a learning management system (LMS). Workers can opt for training, build development plans, and view career paths for growth in an organization.
- Performance management: Apart from LMS, HCM enables you to conduct performance reviews and manage feedback.
- Advanced analytics: HCM provides more strategic features for you to plan the company’s growth, such as survey capabilities, workforce planning modules, and AI features to benchmark salaries/compensation.

What does it mean when an HRIS integrates with existing tools?
When an HRIS integrates with existing tools, it means the system can connect and share data with other software your company already uses—automatically and seamlessly—without requiring manual input or duplicate data entry.
HRIS integrations typically include:
- Payroll systems: Send employee data (hours, salaries, deductions) directly to payroll providers.
- Accounting platforms: Sync compensation, tax, and benefits data for financial reporting.
- Applicant tracking systems (ATS): Transfer new hire information into the HRIS for onboarding.
- Time-tracking or scheduling tools: Pull in attendance, PTO, and hours worked.
- Communication platforms: Enable workflows or notifications in Slack, MS Teams, etc.
- Learning management systems (LMS): Sync training data and completion records.
- Identity and access management: Provision access to systems automatically when someone joins or leaves.
How does an HRIS work?
An HRIS works by centralizing all workers’ information in a single platform, typically with cloud storage. It allows HR and managers to access worker information from anywhere, and also automates basic HR processes like document, leave, and policy management.
What data is stored in an HRIS?
An HRIS stores workers’ personal and contact information, payroll and benefit details, and time/attendance entries. Apart from the worker information, HRIS also saves all company policies and handbooks in one place.
What are examples of HRIS systems?
Some common examples of HRIS platforms are Deel HRIS, HiBob, Personio, BambooHR, Workday HCM, and ADP Workforce Now. These HRIS platforms stand out for the following reasons:
- Deel: Supports growing organizations across locations and countries to store all workers’ (employees, contractors, or freelancers) data in one place.
- HiBob: Provides a social media-style people directory with a built-in applicant tracking system.
- Personio: Covers core HR tasks, like worker data management, time off tracking, and onboarding. Best suited for small and medium businesses, especially in Europe.
- BambooHR: Provides a modern and intuitive user interface that promotes self-service. Recommended for startups and organizations with 20–300 staff.
- Workday HCM: Supports large enterprises and fast-scaling big businesses, typically those with 1,000+ staff to automate HR functions.
- ADP Workforce Now: Enable mid-market organizations to handle HR, payroll, benefits, time tracking, talent management, and compliance.
Read more: Check our in-depth analysis of the top HRIS solutions on the market.
When should an organization get an HRIS?
It’s the right time for your company to get an HRIS when you’re juggling multiple spreadsheets to find simple worker details. HRIS combines all workers’ data, automates workflows, and helps HR teams to focus on people, not paperwork.
What is HRIS implementation?
An HRIS implementation requires you to migrate existing data, set up company policies, and enable settings to automate HR workflows. Here are the detailed steps:
- Collect existing worker data: Combine all your full-time employees, contractors, or freelancers’ data in a single CSV file to upload to HRIS.
- Configure HRIS: Define the data fields that you’ll upload to the HRIS.
- Clean and upload worker data to HRIS: Ensure all the data is in the expected format, and then upload it to HRIS.
- Upload company policies: Upload all your company policies to the portal.
- Set up workflow configurations: Set up the workflow configurations as per company policies. For example, the number of working hours, leaves, etc. Once the configurations are done, you can enable the workflows.
- Define onboarding and offboarding protocols: Define processes to upload or archive worker data when any worker onboards/offboards.
Read more: Learn steps to migrate data to a new HRIS and validate migration using a quick HRIS implementation checklist.
What are the challenges of implementing an HRIS, and how can they be addressed?
Implementation of HRIS has its own challenges that typically happen during the transition phase. Top challenges include:
- Incomplete data migration: Transferring data from your existing system to HRIS can be challenging, especially if your existing data is scattered. You can plan this data migration in multiple steps to ensure nothing gets missed.
- High resistance to change: One-time data migration is not enough. HRIS works well only if all the latest data is available in the portal. So, you must set up processes to update HRIS whenever a worker onboards/offboards or a policy changes.
- Insufficient integrations: An HRIS that is not able to integrate with your tech stack, such as payroll or project management tools, will make the migration and execution tougher. When selecting an HRIS, verify that it integrates seamlessly with your existing tools. That means either it has in-built integrations or APIs available to connect with your HR and finance systems.
- High implementation costs: An HRIS can get costly as you need more advanced features to manage your workforce. It is best to choose an HRIS that allows you to start with a basic plan and subscribe to advanced features as your business grows.
- Rising data security concerns: Worker data is sensitive, and migrating it to any platform does bring that fear of getting non-compliant with data security standards. You must review the HRIS portal and its compliance policies in advance.
How can HR managers measure the ROI of an HRIS implementation?
You can measure the return on investment (ROI) of an HRIS implementation by tracking these metrics:
- HR operations efficiency: Evaluate time saved on HR administrative tasks, such as onboarding, leave approvals, timesheet management, and more.
- Labor cost savings: Assess the labor cost savings in HR operations due to automation of data entry, approval, and audit preparation tasks.
- Reduced compliance error costs: Quantify the reduction in compliance fines due to data entry mistakes.
- Worker satisfaction: Conduct surveys to gauge worker satisfaction with the new HRIS system. Increased worker satisfaction pays off in the long run with high engagement and low turnover.
Manage your global workforce compliantly with Deel
Deel is an all-in-one HR platform with HRIS, HRMS, and HCM capabilities. But the good news is you don’t have to sign up for everything from day one.
Deel HRIS is a good place to get started. It helps you manage worker data across 150+ countries compliantly. You can start with the basic plan, which provides:
- Worker directory: Store and secure employee data centrally and ensure consistent, accurate data across contracts, tax forms, and payroll records
- Job architecture: Get the organization hierarchy with levels, titles, profiles, salaries, and required competencies for every role.
- Onboarding: Ensure that new hires complete local compliance forms, such as tax declarations, before their first payroll cycle.
- Offboarding: Automatically generate termination documents, calculate final pay based on remaining leave balances, and ensure compliance with local offboarding laws.
- Time and attendance management: Track work hours, attendance, and overtime, and feed this information directly into payroll and compliance systems.
- Customization and workflow automation: Enjoy flexible customization options for workflows, approvals, and notifications to match your organization’s unique HR processes.
- Workforce analytics and planning: Leverage robust analytics for strategic workforce planning, diversity tracking, and HR reporting
- Seamless integrations: Get native or easy-to-integrate connections with other enterprise systems (accounting, equity, expense management, issue tracking, SSO, and many more) to create a unified ecosystem
- AI: Drive efficiency with AI with instant answers on labor laws, generating reports, creating training courses, and more.
As your business grows, you can sign up for advanced capabilities to handle global payroll, benefits management, learning and development, performance feedback, compensation planning, and workforce planning.
Reach out to our experts to build a customizable subscription plan suited for your business.
