Article
11 minutes
How to Create a Skills Matrix for Your Teams in 9 Steps
Global HR

Author
Lorelei Trisca
Last Update
January 31, 2025

Table of Contents
Step 1: Define the objective of your skills matrix
Step 2: Define the scope of the skills matrix
Step 3: Identify the necessary skills in your organization
Step 4: Create the matrix structure and rating system
Step 5: Collect data on current employee skill levels and populate the matrix
Step 6: Analyze the results
Step 7: Develop an action plan to address gaps
Step 8: Review and update the matrix regularly
Step 9: Leverage the skills matrix data for other HR processes
Tools for creating a skills matrix (+ Free templates)
Assess and develop employee skills with Deel Engage
Key takeaways
- A skills matrix provides a clear visual representation of a team’s competencies. This helps enhance productivity, minimize skill gaps, and ensure that every member is equipped for success.
- By regularly assessing and updating the skills matrix, organizations can track individual and team progress, identify emerging skill gaps, and proactively address training needs.
- Use Deel Engage to create and manage your skills matrix: You can speed up collecting and analyzing skills data to incorporate regular updates and feedback.
Using a skills matrix within your organization can help you enhance your team’s productivity, minimize skill gaps, and ensure that every member is equipped for success—all while having an easy-to-use visual representation of your team’s competencies.
In this article, you’ll get a step-by-step guide on creating a skills matrix that leaves no unanswered questions. We’ve also included concrete examples at every step to help you understand exactly what you need to do next.
Step 1: Define the objective of your skills matrix
The primary goal of a skills matrix is to provide a visual representation of the skill sets and competencies available within a team or organization. It helps:
- Identify skill gaps
- Support targeted employee development
- Ensure the proper allocation of resources for optimal team performance and strategic growth
- Enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of workforce planning and talent management
A skills matrix focuses on professional growth and aims to enhance team capabilities, support career development, and align skills with strategic goals. This approach improves employee retention and ensures the organization is equipped to meet future challenges.
Some other business objectives you can set when creating a skills matrix include:
- Enhancing team capabilities and tailoring training programs to meet individual career aspirations
- Supporting career development and clarifying potential career trajectories
- Efficiently assigning staff to projects based on skill availability and capacity
- Aligning skills with strategic goals and identifying complementary skills across teams
- Ensuring you have qualified individuals ready to fill key roles as they become available
- Using skills data to refine workflows and reduce inefficiencies
- Promoting flexibility and adaptability in response to changing business needs
Deel Engage
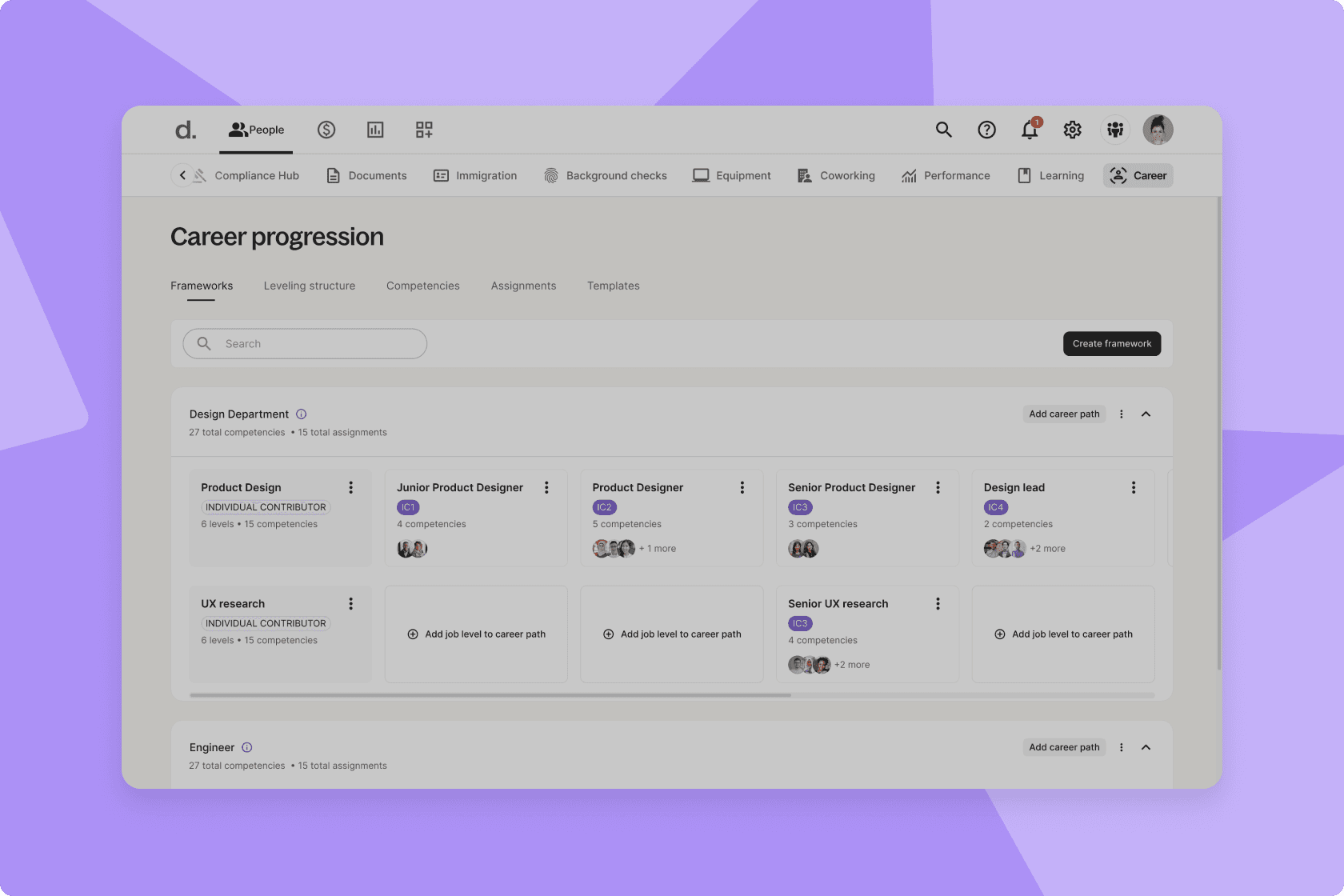
Step 2: Define the scope of the skills matrix
The second step in creating a skills matrix is to define its scope—whether it will be focused on role-level, departmental, or organizational needs.
- Role-level matrix: Focuses on specific job roles and detailing the skill sets required for each—this approach is beneficial for roles with unique or highly specialized requirements
- Departmental matrix: Covers skills within a particular department—this makes it ideal for larger organizations where teams have distinct functions and need tailored skill assessments
- Organizational matrix: Encompasses skills across the entire organization, providing a comprehensive view of all employees’ competencies.
The choice between these scopes largely depends on the organization’s objectives and size.
Let’s consider two examples
In a startup with about 30 employees, a single skills matrix can effectively capture the competencies of all staff due to the company’s small size and simpler structure. This simplifies management and provides a holistic view of each employee’s skills, making it easier to identify areas for growth.
For a growing company with 300 employees, creating separate departmental or team-level matrices is advisable. A single matrix in this context would be overwhelming and complex to manage. It would make it challenging to pinpoint specific skill gaps or development needs within different teams, leading to inefficiencies and a lack of targeted insights.
Don’t forget the scope of the skills matrix is also closely tied to the organization’s objectives picked for step one. A comprehensive organizational view is necessary if the goal is to align existing employee skills with strategic business goals. This may involve creating a single document for smaller organizations or multiple departmental matrices for larger ones.
By defining the scope accurately, the skills matrix can:
- Serve as a strategic tool to enhance workforce planning
- Support career development
- Align employee capabilities with the company’s long-term goals

Skills matrix on Deel Engage
Step 3: Identify the necessary skills in your organization
To create an effective skills matrix, it’s essential to identify and list all the skills and competencies required across various dimensions of your organization. This includes specific projects, individual roles, departments, and the organization as a whole.
You should consider:
- Soft skills like communication, team leader capabilities, and emotional intelligence
- Hard skills such as technical abilities and specialized knowledge
This comprehensive approach ensures that all critical capabilities are accounted for, promoting a well-rounded and skilled workforce.
Tip: Use your organization’s competency model as a reference for this step. A competency model offers a structured outline of the essential skills and behaviors needed for different roles and competency levels within your company. It is a valuable tool for capturing relevant skills aligned with your organization’s standards and strategic goals.
To further refine this process, look closely at the new skills needed for different roles within your team or department. Identify both the core skills crucial for success in a particular role and additional skills that would be good to have.
For instance, a content marketing manager should be proficient in content marketing strategy, copywriting, and SEO fundamentals. However, basic graphic design and video editing skills would also be beneficial.
A good starting point for determining which skills to evaluate is your company’s career framework. This framework is a written definition of each role’s core competencies, including:
- Soft skills: Communication, teamwork, problem-solving, emotional intelligence, etc.
- Hard skills: Job-specific technical skills such as web analytics, SEO, data analysis, etc.
- Values: How an individual embodies the organization’s values and cultural principles.
Organizations vary in how they approach this. Some maintain a single, generic competency model for all roles, offering a broad overview. Others develop detailed progression paths for every role and level, providing a clear roadmap for career development within the organization.
If your company doesn’t yet have any of these prepared, access our free templates to start using your own:
- Competency Framework Template
- Leadership Competency Framework Template
- Core Competency Matrix Template
Step 4: Create the matrix structure and rating system
Create a matrix with roles or individual employees listed along one axis (rows) and skills listed along the other axis (columns). This format allows you to visualize the skills possessed by each role or employee.
Ensure all relevant skills identified during step three are included as column headers. This may contain hard and soft skills essential for roles or projects within your organization.
Establish a rating system to evaluate proficiency levels for each skill. Keep the rating scale clear and intuitive to facilitate accurate assessments.
Example rating system:
- Level 0: No skill
- Level 1: Beginner
- Level 2: Proficient with some oversight
- Level 3: Independent proficiency
- Level 4: Expert and a mentor sought out for expertise
Limit the rating scale to a maximum of five levels, as recommended by Laura M. Hume to ensure distinctions remain meaningful without becoming overly granular:
My recommendation is to not go beyond five levels when assessing skill proficiency. Once you exceed five, the distinctions become too granular and not meaningful. Distinguishing between levels like six and seven, even with well-defined behavior statements, is overly detailed. You generally need more than three levels to allow for progression over many years. I suggest four or five levels.
—Laura M. Hume,
Executive Consultant & Strategic Advisor
Alternatively, you should define a color grading system to visually represent particular skill proficiency levels. This will help create a heatmap-style visualization of skill distributions and gaps across the matrix.
Example color grading system:
- Red: Indicates low proficiency levels (e.g., Level 0 to 1)
- Yellow: Represents developing proficiency (e.g., Level 2)
- Green: Signifies high proficiency levels (e.g., Level 3 to 4)
Step 5: Collect data on current employee skill levels and populate the matrix
One of the most common ways to create a skills matrix is via Excel. Follow the below steps to create a skills matrix in an Excel document:
- Create a table or matrix with the skills listed in the first column and name it “Skills”
- Write down the team members’ names horizontally in the column “Employee name”
- Create the columns “Expertise” and “Interest” under Name
- Add the data on expertise and interest levels collected earlier
Doing this will give you an overview of each employee’s abilities and skill level. Sort the skills into categories based on their contribution to practical project completion.
You can evaluate the current skill levels of all team members through self-assessments, peer reviews, or manager evaluations.
Complimentary resource
To enhance your skills matrix implementation, get detailed guidance on assessing skills and competencies.
Step 6: Analyze the results
Once your skills matrix is populated, examine the completed matrix to identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps that need addressing.
Tip: Involve key stakeholders from each department to ensure diverse perspectives and insights.
Conduct a calibration session where stakeholders review and validate assessment data for consistency and accuracy. Then, you can collaborate on action plans to address identified gaps and leverage strengths effectively across the organization.
What to focus the analysis on:
- Identify skills gaps and training needs:- Highlight areas where multiple employees lack proficiency, indicating a need for training
- Identify internal subject matter experts:- Identify highly skilled employees who can be mentors or trainers. [If this is an objective, one of the rating scales can be “constantly exceeds expectations” or “sets a new standard” to differentiate the top “skill masters”
Step 7: Develop an action plan to address gaps
Based on the analysis, create a plan for training, hiring, or reallocating resources to bridge any identified skill gaps.
For instance, you can start planning new training initiatives:
- Schedule workshops to address common skill deficiencies
- Partner with training providers to design tailored courses for certifications
- Provide online learning options for flexibility
You can also consider setting up mentorship programs. These allow you to pair less experienced employees with experts for on-the-job learning. This facilitates knowledge transfer, preparing your team for future challenges and aiding succession planning efforts.
Learning Management
Step 8: Review and update the matrix regularly
Establish a systematic review and update process to maintain the skills matrix’s relevance and effectiveness. Regular updates ensure the matrix evolves with changing business needs, technological advancements, and employee development.
Consider establishing a feedback loop process to incorporate feedback from employees and managers to refine the matrix. Use anonymous feedback tools to encourage honest responses and review feedback to identify common themes or areas for improvement.
Complimentary resource
Learn how to create an effective employee feedback system for your organization.
Step 9: Leverage the skills matrix data for other HR processes
Use the data from the skills matrix to inform other HR processes such as employee performance reviews, succession planning, and recruitment. Integrate this list of skills matrix data with other HR systems and processes to ensure a holistic approach to talent management.
Some examples of how the integration can look like are:
- Succession planning: Identify high-potential employees and plan their career paths based on their required skills and competencies—this makes for a seamless transition when key personnel leave and motivates employees by providing a clear career progression roadmap for growth within the organization
- Recruitment: Align hiring process criteria with the skills your organization needs (as identified in the skills matrix)—this targeted approach ensures that new hires bring the specific skills required, fostering a balanced and high-performing team
- Learning and development: Align the skills matrix with ongoing training and development plans and programs—following this approach ensures your employees know what you expect from them and where they stand compared to your expectations for their specific role
Tools for creating a skills matrix (+ Free templates)
Various tools offer the flexibility and functionality needed to create an effective skills matrix, simplifying the process. Classic solutions such as Excel and Google Sheets are highly customizable with numerous formatting options. Pivot tables and charts further support visual data representation that’s easy to share and accessible from any device.

Complementary resource: Get our skills gap analysis template for a more in-depth analysis considering skill importance and proficiency.

These free templates are a great resource, especially for smaller organizations creating or improving their HR processes. However, for growing organizations, juggling multiple Excel sheets and documents with policies and training plans is not time or cost-effective. You will have to:
- Get input from all stakeholders and teams
- Ensure said data is valid and fair
- Constantly worry about accidentally messing up anything in Excel
- Keep the matrix up-to-date
Manual skills matrices quickly get overwhelming and complex to manage, making it challenging to pinpoint and reference specific skill gaps or development needs within different teams. In such cases, software solutions will offer a better alternative. Deel Engage is a software solution that will automate and increase the efficiency of your skills matrices and overall talent management processes.
Assess and develop employee skills with Deel Engage
Deel Engage helps organizations:
- Get valid, unbiased data via customizable feedback forms to build high-performing teams
- Automatically engage all stakeholders - send reminders with a slick if reviewers fall behind on their assessments
- Calibrate your skill assessment data to ensure consistency across the organization
- Scrutiny your automatically generated skills matrix once the review cycle is complete
- Automatically keep your skills matrices up-to-date with regular feedback cycles (performance review, etc.)
- Use bar and radar charts, 9-box grid, or skills matrices to stay on top of goal progress, identify high potentials, and uncover development opportunities
- Give your people a roadmap for professional growth and keep your team motivated
- Train your people with internal and external courses
Build a highly-performing team and better assess your team’s skills with Deel Engage. Request a demo today.
FAQs
What is a skills gap matrix?
A skills gap matrix is a tool organizations use to identify and track the differences between employees’ skills and those needed to meet organizational objectives or job role requirements. Creating a skills gap matrix helps pinpoint specific areas where skill development is needed, helping you make data-driven decisions on training, hiring, and resource allocation.
What is the difference between a skills matrix and a competency matrix?
A competency matrix maps the required competencies against specific organizational roles or individuals, visually representing which competencies are necessary for each role and at which proficiency levels. Meanwhile, a skills matrix maps specific skills against employees to identify available skills and skill gaps.
Explore our in-depth analysis of the competency vs. skills matrix, where we showcase how using both simultaneously provides a comprehensive framework for assessing, developing, and leveraging talent within your organization.
What is the next step after creating a skills matrix?
After creating a skills matrix, the next step is to use it to inform decision-making. This might mean using the matrix to identify your worker’s missing skills and creating development plans to address those gaps.
Alternatively, use skills matrices to assess internal job candidates or to determine which team members are best suited to work on a particular project.
How can skills matrix software help?
Skills matrix software helps streamline the creation and maintenance of a skills matrix. Using software to automate the process saves HR teams time and reduces the risk of errors. Additionally, skills matrix software solutions like Deel Engage offer advanced reporting and analytics features to gain insights into any team’s skills and identify areas for improvement.
How can a skills matrix support remote work?
A skills matrix supports remote work by:
- Clearly defining the skills required for remote roles
- Identifying employees who are well-suited for remote work based on their skills
- Facilitating the integration and onboarding of remote workers by aligning their skills with team needs
- Ensuring consistent skill assessment and development opportunities for remote employees
- Enhancing communication and collaboration in remote teams by making everyone aware of each other's skills
What are the best practices for maintaining a skills matrix?
Best practices for maintaining a skills matrix include:
- Regularly updating the matrix to reflect changes in skills, roles, and organizational needs
- Involving employees in the assessment process to ensure accuracy and buy-in.
- Using a standardized rating scale to maintain consistency
- Integrating the skills matrix with other HR tools and systems for seamless data management
- Analyzing the matrix periodically to identify trends, gaps, and areas for improvement
By addressing these questions, HR specialists can effectively utilize a skills matrix to enhance workforce planning, improve team performance, and support strategic organizational goals.
More resources

About the author
Lorelei Trisca is a content marketing manager passionate about everything AI and the future of work. She is always on the hunt for the latest HR trends, fresh statistics, and academic and real-life best practices. She aims to spread the word about creating better employee experiences and helping others grow in their careers.