Article
15 minutes
How to Conduct a 9-Box Assessment for Talent Management Step-by-Step
Global HR

Author
Lorelei Trisca
Last Update
January 24, 2025

Table of Contents
Step 1: Define criteria for performance and potential
Step 2: Define data collection methods
Step 3: Define 9-box assessment questions
Step 4: Train stakeholders on the 9-box methodology
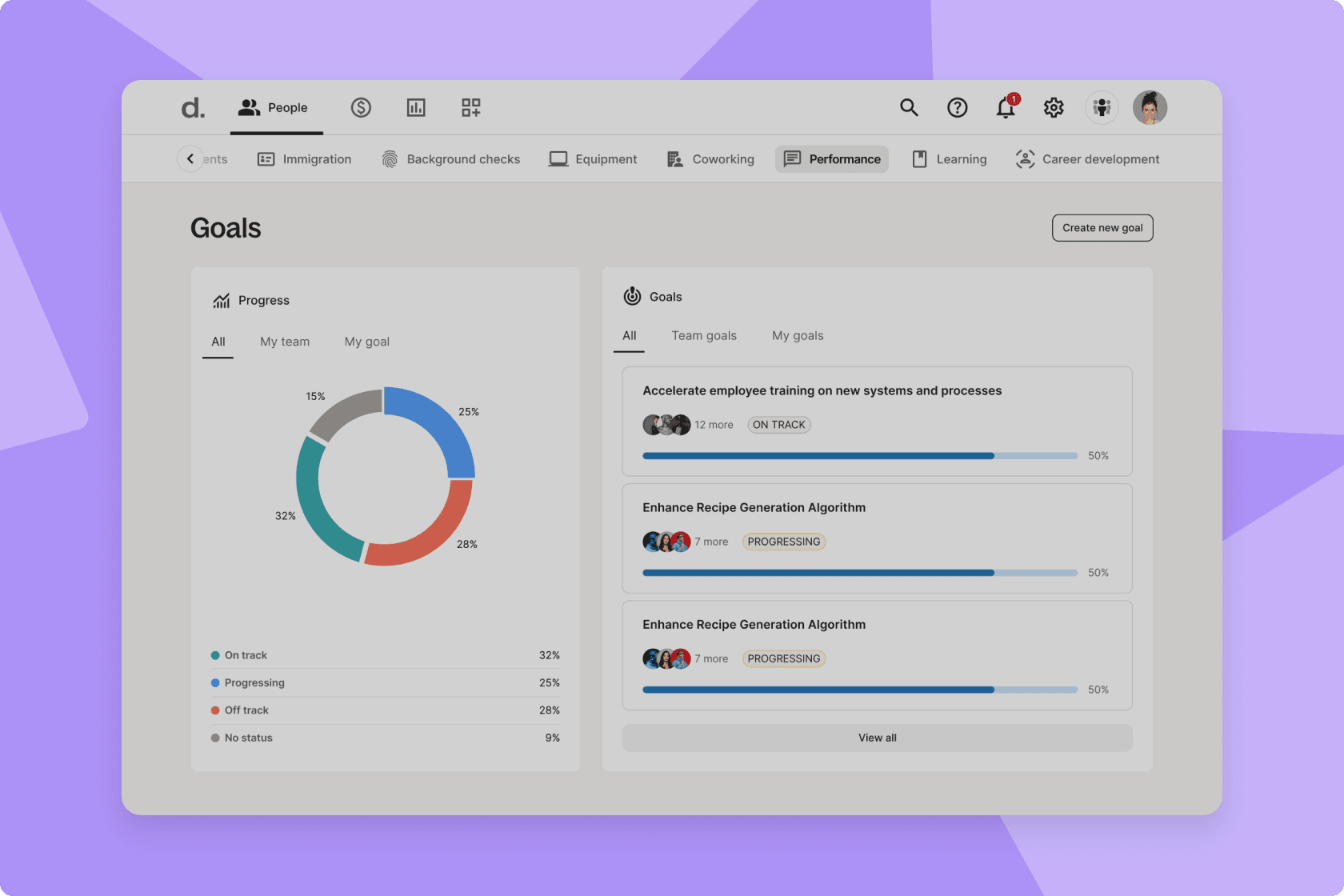
Step 5: Collect data and sort employees into categories
Step 6: Analyze the results
Step 7: Define strategies for developing employees in each category
Step 8: Take action based on the assessment
Free 9-box assessment template
Best practices for successfully conducting 9-box assessments
Ensure strategic talent management with Deel Engage
Key takeaways
- The 9-box grid is a strategic talent management tool used to identify high-potential employees and develop them effectively.
- Provide comprehensive training for evaluators to ensure consistent application of the 9-box model and reduce bias.
- Software tools like Deel Engage offer a better and faster method for initiating your 9-box assessment process.
The 9-box grid model is widely used in talent management to assess and categorize employees based on their performance and potential. While its fundamental structure remains consistent, the model’s adaptability makes it highly versatile. You can tailor the labels of each of the nine categories to align with their corporate language and objectives, making the model uniquely suited to their needs.
At its core, the 9-box grid intersects three performance tiers with three levels of growth potential, creating a matrix that offers a detailed snapshot of each employee's performance and future potential. This provides a clear framework for decision-making in areas like talent development, succession planning, and performance management.
Take an in-depth look at all the steps to run an effective 9-box assessment.
Step 1: Define criteria for performance and potential
These levels form the foundation for the 9-box grid, enabling you to strategically manage talent based on both current performance and future potential.
Performance
Define the 9-box assessment criteria for evaluating employees, categorizing performance into three categories:
- Low performance: The employee hasn’t met the job responsibilities or individual performance goals
- Average performance: The employee has partially fulfilled job responsibilities and performance goals
- High performance: The employee has met all job responsibilities and individual performance goals
You may use various criteria to define these levels, such as focusing on individual performance goals, job responsibilities, or a combination of both.
Potential
Employee potential reflects an employee's ability to develop and advance within the organization. It can be categorized using the following levels:
- Low potential: The employee is performing to the best of their ability, but lacks motivation or shows limited potential for growth
- Average potential: The employee demonstrates the ability to grow within their current role and shows potential for improving performance or developing their skills
- High potential: The employee exceeds expectations and exhibits enthusiasm for leadership roles, making them strong candidates for promotions and future development opportunities
Outline the characteristics associated with the growth potential levels you have established. This will provide a clear framework for assessing where each employee aligns with these categories.
For instance, consider the traits of an employee with high potential. Such individuals typically demonstrate a strong commitment to self-improvement, actively seek learning opportunities, and apply new knowledge to their work. Their drive for advancement is often evident through the following behaviors:
- They have fully used the training budget allocated to them for the year or quarter
- They have proactively requested sponsorship for a professional certification program
- They have independently enrolled in internal training programs offered by the organization
- They have expressed a clear desire to advance within the company
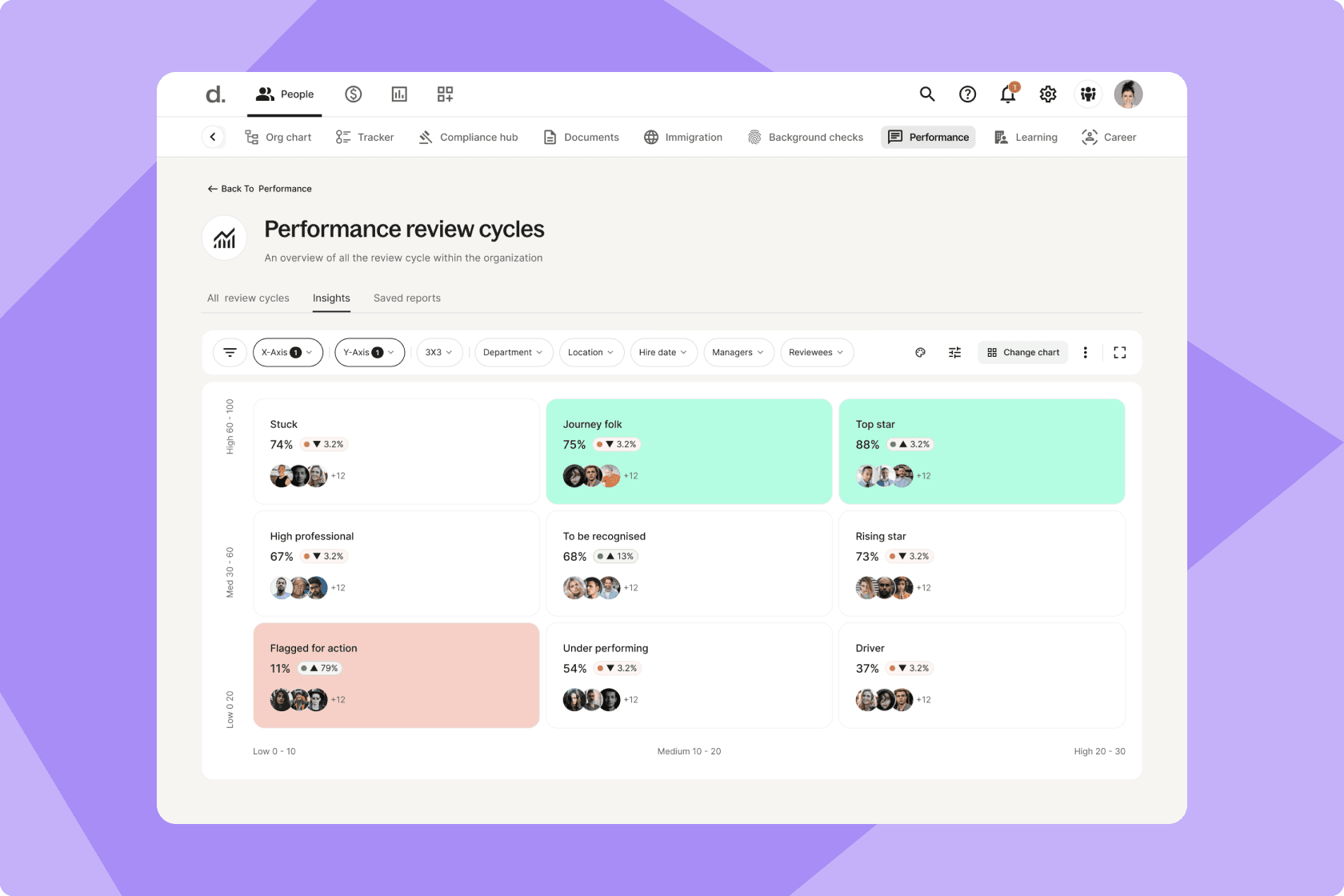
9-box grid on Deel Engage
Step 2: Define data collection methods
To implement the 9-box grid assessment correctly, collect diverse types of data to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
Essential data sources include annual performance reviews, which provide a formal assessment of employee achievements and improvement areas.
In addition, peer feedback offers valuable insights into an employee’s interactions and effectiveness within their team. Self-assessments allow employees to reflect on their performance and growth potential from their perspective.
Gather this data systematically by scheduling regular performance reviews, soliciting peer feedback through structured surveys, and encouraging employees to complete self-assessments. Ensure data is collected consistently across the organization to maintain fairness and accuracy in the evaluation process.
For additional guidance on employee performance evaluation methods and best practices, visit our detailed guide.
Performance Management
Step 3: Define 9-box assessment questions
When assessing employees, refer to the performance goals set by their managers. These goals should reflect the employee’s job responsibilities and provide a clear framework for evaluating performance. If there is a disconnect between performance goals and actual job responsibilities, review relevant job descriptions or consult with managers to obtain accurate, up-to-date information.
In addition to this approach, consider using specific, tailored assessment questions to guide your evaluation process.
Below are examples of targeted questions that can help assess both performance and potential in the 9-box grid:
- Current performance: How well is the employee performing in their current role? Are they meeting, exceeding, or falling short of expectations?
- Role evolution: How has the employee's role or responsibilities evolved over time? Have they taken on new challenges or responsibilities?
- Growth and development potential: What is the employee's potential for growth within the organization? Are they ready for more advanced roles or additional responsibilities?
- Performance and potential comparison: How does the employee’s performance and potential compare to peers at the same level? Are they considered a high performer within the team?
- Leadership potential: Does the employee demonstrate strong leadership potential? How well have they taken initiative or led projects?
- Alignment with organizational goals: How well does the employee’s performance and behaviors align with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives?
- Cultural and value fit: Does the employee consistently demonstrate a commitment to the company’s core values and culture?
- Skill proficiency: How proficient is the employee in both technical skills and soft skills (communication, teamwork, adaptability)?
- Adaptability and change management: How well does the employee adapt to change, uncertainty, or new challenges? Do they show resilience in difficult situations?
- Problem-solving and project management: How effectively does the employee handle complex or challenging projects? Do they demonstrate problem-solving abilities under pressure?
Get more inspiration for collecting feedback for performance reviews:
Step 4: Train stakeholders on the 9-box methodology
Regularly review your assessment methodology to ensure consistent and accurate application of the 9-box model. For new team members unfamiliar with the model, offer comprehensive training that explains how your organization uses it to evaluate employee performance and potential.
Training should cover the basics of the model, with a focus on defining performance and potential criteria specific to your organization. Use practical examples, real-life scenarios, and interactive discussions to help clarify these concepts, allowing participants to practice applying the model to different employee profiles.
For the rest of your team, refresh their understanding of the criteria used to assess performance and potential. This could involve a pre-evaluation workshop held one or two weeks before the assessment period. During this session, provide detailed examples and encourage managers to share their experiences and insights, helping to ensure that everyone approaches the evaluation with a shared understanding.
To ensure all managers share a common understanding of the 9-box model:
- Administer a short test at the end of the training session to assess their comprehension of the performance and potential criteria—this could involve categorizing hypothetical employees and explaining their rationale
- After the evaluations, hold a calibration meeting where managers can compare their assessments to ensure consistency and alignment across the organization
- Provide ongoing feedback to managers throughout the evaluation period to address any discrepancies or confusion in the assessment process
Learning Management
Step 5: Collect data and sort employees into categories
Ranking employees using the 9-box grid allows you to determine their precise position within the matrix. It’s essential to involve managers, team leaders, and, if appropriate, directors and other senior executives in this process.
The involvement of these stakeholders is crucial to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of each employee's performance and growth potential while minimizing unconscious biases.
Assess employees within each team before proceeding to the next department. Ensure that all teams in the current department are evaluated thoroughly before moving forward.
Our 9-box grid template automates the calculations and placements, making the process easier and faster for you.
Step 6: Analyze the results
To analyze the results of a 9-box grid assessment, start by reviewing the distribution of employees. Identify if there are clusters of low performers or individuals with low potential. Too many in these categories may signal a need for development programs or reassessment of hiring strategies. If no employees are marked with leadership potential, it could indicate gaps in leadership pipelines.
Key issues to spot include:
- Low performance paired with low potential: Discuss future steps, such as reassignment, upskilling, or possible exit strategies
- High performance paired with low potential: These employees are reliable but may not grow further; recognize and reward their contributions
- High potential paired with low performance: Consider development opportunities, coaching, or role changes to unlock potential
Identify employees deserving salary increases, bonuses, or promotions based on consistent high performance and growth potential. Average performers, especially those with medium-high potential, may benefit from role or project changes to foster growth.
Step 7: Define strategies for developing employees in each category
With a 9-box grid, it's crucial not just to label each box but also to define the strategies needed for developing employees within each category. Below are approaches for managing employees based on their position in the performance-potential matrix.
Low performance, low potential
Development strategy:
- Identify obstacles hindering performance and growth
- Avoid excessive resource allocation toward these employees, ensuring company resources are not strained
- Monitor their progress to prevent other employees from falling into this category
- If they exhibit enthusiasm for switching roles, consider offering a position better suited to their skills
Average performance, low potential
Development strategy:
- Exercise caution when providing extensive training or resources
- Develop a personalized performance improvement plan to address gaps
- Regularly track their progress and document any improvements
High performance, low potential
Development strategy:
- Focus on maintaining job satisfaction to retain these employees in their current roles
- Avoid over-investing in promotions, salary increases, or high-responsibility positions, as their growth potential is limited
- Encourage them to pursue further self-development and prepare them for upcoming organizational changes
Low performance, average potential
Development strategy:
- Diagnose the root causes of underperformance
- Implement targeted coaching or mentoring programs
- Monitor progress closely and record improvements
Average performance, average potential
Development strategy:
- Clearly communicate job expectations and ensure alignment with their role
- Keep them motivated and satisfied through regular feedback
- Provide diverse training opportunities, both in-person and online, to expand their skill set
- Consider job rotations or broadening responsibilities to increase engagement.
- Regularly recognize their achievements and assess their performance
High performance, average potential
Development strategy:
- Engage with these employees regularly to gauge satisfaction and foster long-term commitment
- Sustain high performance by recognizing achievements and offering challenging opportunities
- Allow time for them to reach their full potential and consider job rotations or task delegation to expand their responsibilities
- Provide advanced training or mentorship to unlock further potential
Low performance, high potential
Development strategy:
- Set clear role expectations and allow a reasonable period for performance improvement
- Provide coaching or training aimed at leveraging their high potential
- Closely monitor their performance trajectory and ensure noticeable progress within a defined timeframe
Average performance, high potential
Development strategy:
- Exhibit patience as they work toward improving their performance, recognizing that they possess the potential to grow
- Identify specific training needs and provide targeted development resources
- Continue to follow strategies similar to those for employees with average performance and potential, while planning for long-term growth
High performance, high potential
Development strategy:
- Frequently recognize and reward their efforts, ensuring high levels of job satisfaction
- Assign them complex, challenging tasks to maintain engagement and drive further development
- Consider these employees for leadership roles and integrate them into succession planning
- Provide opportunities for networking and mentorship with senior leaders.
- Offer competitive compensation to retain top talent and ensure they remain engaged within the organization
Deel Engage
Step 8: Take action based on the assessment
Use the 9-box results to make talent management decisions, such as development plans, promotions, or succession planning. Tailor training programs, coaching, and mentoring to meet the specific needs of employees, addressing both performance and potential.
For example, for high performers with leadership potential, craft succession strategies and discuss role expectations with them to prepare for future opportunities.
Enhance the employee experience by refining onboarding processes and ensuring that development plans align with the 9-box model. While some organizations may choose not to disclose growth potential, sharing this information can help employees understand their career trajectories and create a roadmap for improvement.
Tip: Be cautious when discussing promotions. Communicate readiness only when a position is available to avoid raising unrealistic expectations.
Lastly, recognize that high potential paired with low performance often reflects a need for experience or development, so focus on strategies that improve performance without diminishing long-term potential.
Complementary guide
Free 9-box assessment template
Use our 9-box grid template which comes in two versions:
- Simple 9-box assessment template: Select this version if you already have both performance and potential scores on a 1-3 scale
- Advanced 9-box assessment template: Use different rating scales for performance, which are then converted to a 3-point system for the 9-box grid

Free template
Understand your workers' performance and potential
Best practices for successfully conducting 9-box assessments
The 9-box grid model, while highly valuable for talent management, comes with certain limitations. Use our recommended best practices to overcome and prevent the challenges in using the 9-box assessment method.
Ensuring objectivity and reducing bias
Establish clear, predefined criteria for evaluating both performance and potential creates a standard framework, making it easier to assess employees based on consistent measures rather than subjective opinions.
Involving multiple stakeholders in the evaluation process, such as managers and HR leaders, allows for a more balanced view, reducing the impact of individual biases. Collaborative discussions provide diverse perspectives and help arrive at more accurate conclusions.
With the help of data-driven insights (e.g. performance metrics, feedback), you can further reduce subjectivity in the assessment. We also recommend training stakeholders before the assessment so they understand the criteria, process, and importance of minimizing bias.
Involving key stakeholders
Including managers, HR, and other relevant parties in the 9-box assessment process makes for a well-rounded evaluation. Managers provide direct insights into an employee’s day-to-day performance, while HR offers a broader view of talent development and organizational goals. Other stakeholders, such as department heads or project leads, can contribute additional perspectives on potential and leadership readiness.
Involving multiple stakeholders also means you can get diverse viewpoints, which reduces the risk of individual bias too. It also ensures that all parties are aligned on the assessment outcomes and proposed actions. This collaborative approach fosters transparency and promotes buy-in for decisions, such as talent development plans or role changes, ensuring smoother implementation of any changes.
Communicating results and next steps
When sharing the results of a 9-box talent assessment, keep transparency at the core of the process. Explain the employee's placement on the grid, the criteria used, and how their performance and potential were evaluated. This open communication fosters trust and helps employees understand the process.
It's also important to always have the next steps outlined. Discuss development opportunities, training, or coaching based on the assessment results. For high-potential employees, talk about potential career paths or leadership roles. To track progress, set clear key performance indicators (KPIs). Measurable goals give employees a roadmap for improvement and enable managers to monitor development, making it easier to revisit progress in future assessments.
Conducting a calibration session to prevent discrepancies
To prevent discrepancies, hold a performance calibration session. This meeting updates key stakeholders on performance appraisals, expectations, and ratings to ensure consistent evaluations.
During the session, review each employee's placement on the grid, discuss their performance and potential, and compare them with others in similar roles. This collaborative approach ensures ratings are applied fairly and consistently, preventing individual bias or misinterpretation of the criteria.
Learn how you can use a calibration session to create a standardized framework for talent evaluations with our best practices for productive performance calibration meetings.
Ensure strategic talent management with Deel Engage
With Deel Engage, you can establish a performance-driven feedback culture that fosters growth and development. The platform can help you:
- Assess performance and potential with the performance management module
- Automatically populate 9-box grids with the results of performance appraisals (single or multi-rater, depending on your internal processes)
- Train employees to improve their performance and skill sets—develop training courses internally or make use of the external library from world-class providers
- Define career development paths for employees, helping them advance their careers in your company
In addition to these features, the Deel platform has built-in HRIS functionalities available at no additional cost.
Book a demo to discover how our solutions can help you build and sustain a high-performance workforce.
Deel Engage is our all-around tool for career and personal development processes, connecting all the dots at once. This allows us to have a data-driven talent management process.
—Christina Bacher,
Team Lead, People and Organization, reev
FAQs
What is the difference between 9-box assessments and performance appraisals?
9-box assessments evaluate employees based on performance and potential to guide talent management and succession planning. They're used for long-term development and identifying future leaders. Benefits include strategic talent allocation and targeted development plans. Performance appraisals, on the other hand, assess individual achievements against set goals, focusing on past performance. These performance review meetings are used for immediate feedback or promotions and include performance improvement and recognition of accomplishments.
How do you align business goals with 9-box assessments?
Aligning business goals with the 9-box assessment strategy involves engaging all stakeholders, including managers and HR, to ensure a shared understanding of goals and criteria. Regular updates and feedback sessions help adjust the assessment process in real time. Surveys can gather additional insights from employees and peers, ensuring the grid reflects both current performance and future potential accurately.
Why is the 9-box model important?
The 9-box model is important because it provides a framework for evaluating employee performance and potential in a structured and consistent way. It can help organizations identify high-potential employees, develop succession plans, and make decisions about promotions, bonuses, and other forms of recognition.
What is a talent classification matrix?
A talent classification matrix is a tool used to classify employees based on their performance, potential, and other factors, such as skills and behavior. The goal of a talent classification matrix is to identify employees with high potential and high performance and those who may need additional coaching or development to reach their full potential.
Is the 9 grid matrix the same as the high-potential high-performance matrix?
The 9 grid matrix is not necessarily the same as the high-potential high-performance matrix. However, both models are used to evaluate employee performance and potential.
The high-potential high-performance matrix focuses explicitly on employees with demonstrated high potential for growth and development within the organization and high current performance levels.
So, you can consider the high-potential high-performance matrix a subset of the broader 9 grid matrix.

About the author
Lorelei Trisca is a content marketing manager passionate about everything AI and the future of work. She is always on the hunt for the latest HR trends, fresh statistics, and academic and real-life best practices. She aims to spread the word about creating better employee experiences and helping others grow in their careers.